Adulteration Tests
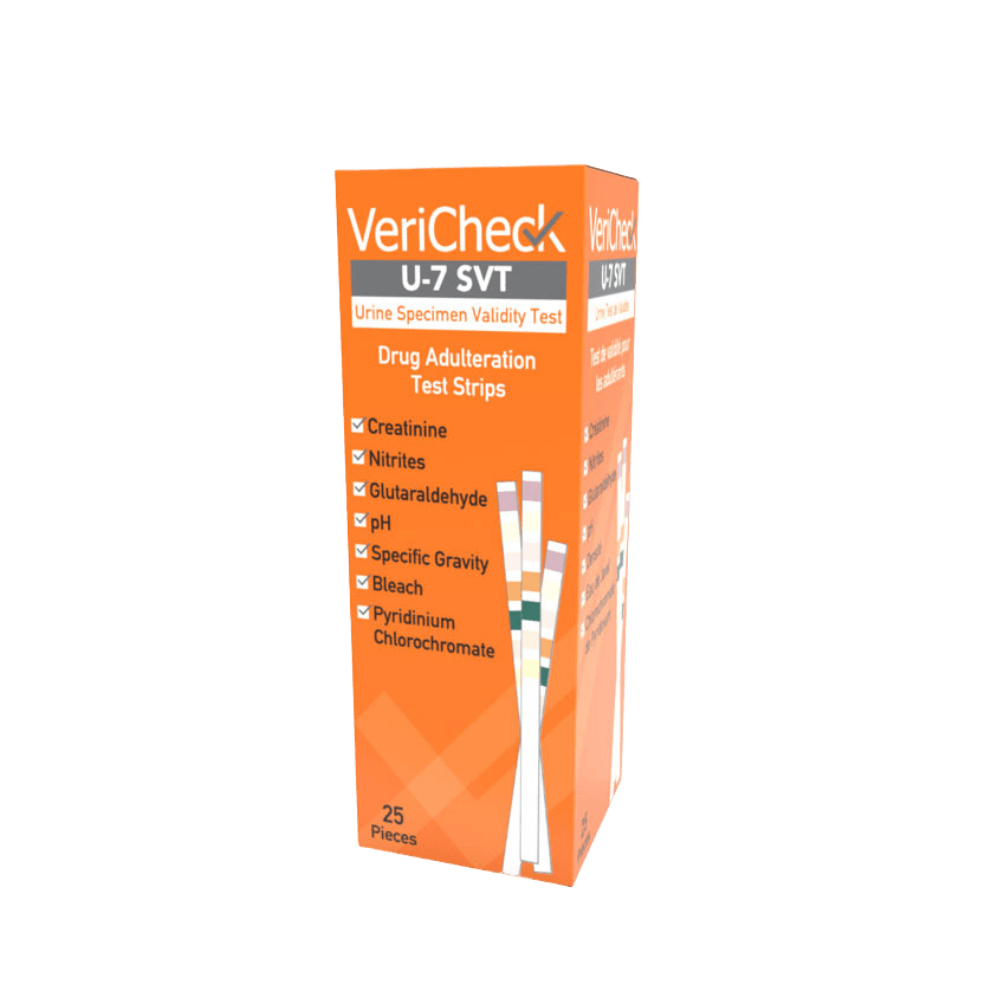
VeriCheck U-7 SVT
+
VeriCheck U-7 Adulteration Test Strips
Quickly testing urine for validity against; substitution, dilution or adulteration is of paramount importance when performing an onsite screening test.
Our strip screens 7 different parameters in less than 60 seconds to ensure that the screening test results can be counted on as accurate.
Specimen Validity Test 7-parameter Adulteration Test Strip
VeriCheck® U-7 SVT test strip provides a 7-parameter screen to confirm the validity of urine for the purpose of screening for drugs of abuse. This test tests: Creatinine, Nitrite, pH, Specific Gravity, Glutaraldehyde, Bleach and Pyridinium Chlorochromate.
ATION The validity of screening urine depends on the integrity of the urine sample. Contaminated or adulterated samples may cause erroneous results leading to significant consequences. Hence, it is important to ensure that the samples are consistent with normal urine. The VeriCheck® U-7 SVT will determine: Whether the sample is diluted or substituted with water or other liquids. Whether the sample contains commercially available adulterants including; Stealth, Urine Luck 6.3 and 6.4, Whizzes, Klear, Clear Choice, Instant additive Lucky Lab, LL418, Purafyzit, Clean or detoxifying cleansers. Whether the sample is contaminated with common household items such as; Drano®, bleach, liquid hand soap or vinegar.
WARNING AND PRECAUTIONS
For in vitro use only.
For informational or forensic use only.
Each test strip is single use only.
The desiccant in the strip container is a non-toxic substance silica gel. If the desiccant is inadvertently ingested, drink water immediately and contact your local poison control center for more information.
Used test strips can be disposed of into the general waste/garbage.
Creatinine: Creatinine reacts with a creatinine indicator in an alkaline medium to form a purple brown color complex. The color intensity of the test pad is directly proportional to the concentration of creatinine in the sample.
Nitrites: The test is based on the diazotization reaction of nitrite with an aromatic amine to produce a diazonium salt. It is followed by an .o-coupling reaction of this diazonium salt with an aromatic compound on the reaction pad. The azo dye produced causes a color change from white to pink.
Glutaraldehyde: This analysis is based on the reaction of the aldehyde group on the glutaraldehyde with an indicator to generate a brown color complex.
pH: Double indicator system. The indicator's methyl red and bromothymol blue are used to give distinct color changes from orange to green to blue.
Specific Gravity (SG): Ionic solutes present in the urine cause protons to be released from a polyelectrolyte. When the protons are released it produces a color change of bromothymol blue from blue-green to yellow-green.
Bleach: If Bleach is detected, a color indicator reacts with it to form a blue complex.
Pyridinium Chlorochromate: A color indicator reacts with pyridinium chlorochromate to form red-violet color.
HANDLING PROCEDURE:
Do not open the container until ready to use.
Close the bottle cap immediately after opening. Keep the bottle tightly closed between tests.
Do not remove desiccant from bottle.
Do not touch reagent pad(s) on the strips.
Keep out of reach of children.
SPECIMEN COLLECTION AND HANDLING
Use a clean dry container to collect the urine specimen and test it as soon as possible. If testing cannot be done within an hour after voiding, refrigerate the specimen immediately and let it retum to room temperature before testing. Improperly stored urine specimens (e.g. urine stored for over 4 hours at room temperature) may produce inaccurate results.
Aliquot the small portion of urine sample into another container in order to avoid contamination of the whole urine sample. Do not dip the test strip directly into the primary collection container.
VISUAL TEST PROCEDURE
The procedure must be followed exactly to achieve reliable results.
Dip the strip into the urine no that all tests areas are immersed for no longer than two seconds.
Draw the edge of the strip along the brim of the container or to remove excess urine.
a. Do not let the test areas touch the container.
Tum the strip on its side and tap it once on a piece of absorbent material to remove any remaining urine.
a. Excessive urine on the strip may cause an interaction of
chemicals between adjacent reagent pads which may cause an incorrect result to be interpreted.
After 60 seconds, compare the test results carefully with the color chart on the vial label under good light. While comparing, keep the strip horizontally to prevent possible mixing of chemicals between adjacent reagent pads
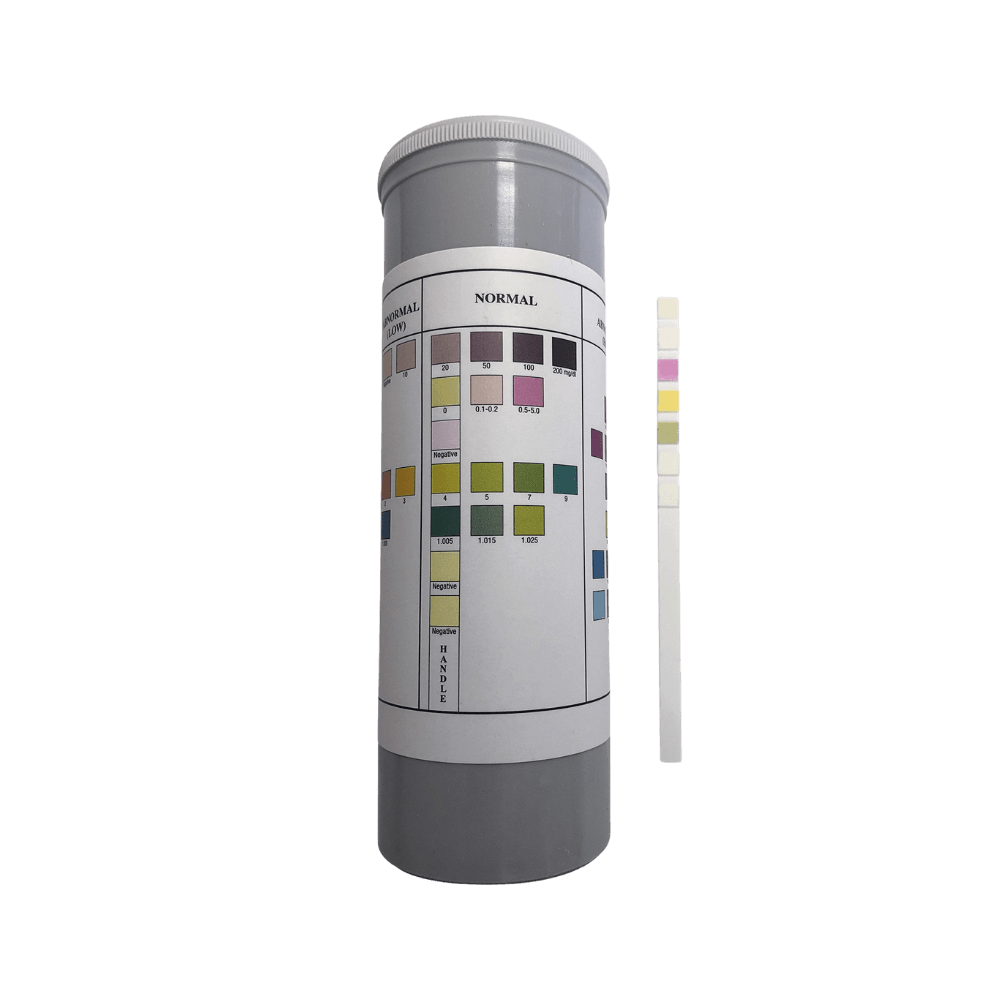
Urine Check 7
+
UrineCheck 7 Adulteration Test Strips
- Ensures the validity of your urine samples
- Detects for adulteration, dilution and substitution
- Simple to use and interpret
- Results in 1 minute
- No instrumentation
- 25 tests per box
The UrineCheck 7 Urine Adulteration Strips are a rapid "dip-and-read” screening test for the determination of diluted or adulterated urine specimens. Adulteration test strips, sometimes known as Specimen Validity Test, (S.V.T.) are a rapid, one step screening test used to determine if a urine sample has been adulterated, tampered with or diluted. The strips simultaneously detects the presence of 7 markers/parameters: Creatinine, Nitrite, Glutaraldehyde, pH, Specific Gravity, and Oxidants/Pyridinium Chlorochromate (PCC) in human urine. The test strips work based on the colour derived from the chemical reaction between the chemical reagent on each test pad and the urine sample, giving a semi-quantitative result via a comparison color chart.
INTENDED USE
UrineCheck 7 is a fast dip-and-read test for the determination of diluted or adulterated urine specimens. It is an important pre-screening test for any drug-testing program. Each bottle contains 25 strips.
SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION
UrineCheck 7 drug adulteration tests are firm plastic strips to which seven different reagent areas are affixed. UrineCheck 7 test strips are ready-to-use and disposable. No equipment is required for its use. Only fresh and uncentrifuged urine samples without preservatives are to be used.
UrineCheck 7 provides tests for Creatinine, Nitrite, pH, Specific Gravity, Glutaraldehyde, Oxidants, and Pyridium Chlorochromate in urine. Test results may be useful for assessing the integrity of the urine sample prior to Drugs-of-Abuse testing; for example, whether the sample is possibly diluted with water or other liquids as indicated by the creatinine and specific gravity tests. UrineCheck 7 detects whether the sample contains commercially available adulterants including nitrite, glutaraldehyde, bleach, pyridinium chlorochromate and other oxidizing agents. UrineCheck 7 can also assess whether the sample is possibly contaminated by acidic (vinegar) or basic (ammonia solution) adulterants as indicated by the pH test.
TEST PRINCIPLE
In general, all seven tests are based on the chemical reactions of the indicator reagents on the pads with components in the urine sample effecting color changes. Results are obtained by comparing the color on each of the test pads with the corresponding pad on the container color chart label.
Creatinine: Testing for sample dilution. In this assay, creatinine reacts with a creatinine indicator in an alkaline condition to form a purplish-brown color complex. The concentration of creatinine is directly proportional to the color intensity of the test pad.
Glutaraldehyde: Testing for the presence of exogenous aldehyde. In this assay, the aldehyde group on the glutaraldehyde reacts with an indicator to form a pink/purple color complex.
Nitrite: Testing for the presence of exogenous nitrite. Nitrite reacts with an aromatic amine to form a diazonium compound in an acid medium. The diazonium compound in turn couples with an indicator to produce a pink-red/purple color.
Oxidants: Testing for presence of oxidizing reagents. In this reaction, a color indicator reacts with oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide, ferricyanide, persulfate, or pyridinium chlorochromate to form a blue color complex. Other colors may indicate the presence of other oxidants.
pH: Testing for the presence of acidic or alkaline adulterant. This test is based on the well-known double pH indicator method that gives distinguishable colors over wide pH range. The colors range from orange (low pH) to yellow and green to blue (high pH).
Specific Gravity: Testing for sample dilution. This test is based on the apparent pKa change of certain pretreated polyelectrolytes in relation to the ionic concentration. In the presence of an indicator, the colors range from dark blue or blue-green in urine of low ionic concentration to green and yellow in urine of higher ionic concentration.
Bleach: Testing for the presence of bleach in urine. In this test, the presence of bleach forms a blue-green color complex.
Pyridium Chlorochromate: Testing for the presence of chromate in urine. In this test, the presence of chromate forms a blue-green color complex.
Procedure
Remove from the bottle only enough strips for immediate use and replace cap tightly.
Completely immerse reagent areas of the strip in fresh, well-mixed urine. Remove the strip immediately to avoid dissolving out the reagent areas.
While removing, touch the side of the strip against the rim of the urine container to remove excess urine. Blot the lengthwise edge of the strip on an absorbent paper towel to further remove excess urine and avoid running over (contamination from adjacent reagent pads.)
Compare each reagent area to its corresponding color blocks on the color chart and read at the times specified. Proper read time is critical for optimal results.
Obtain results by direct color chart comparison.